Understanding Oils and Common Misconceptions
According to the Community Nutrition Improvement Office of the Ministry of Health:
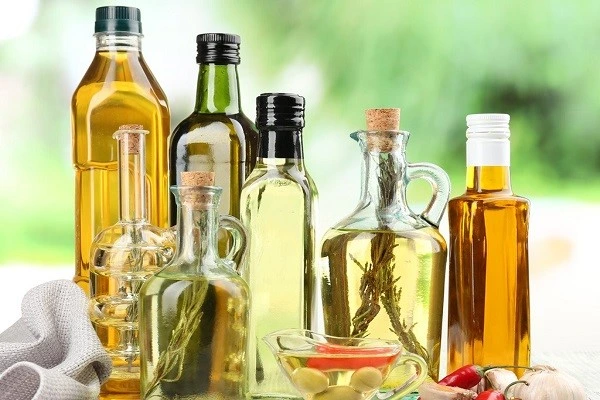
There are many myths and misconceptions about different food groups in society. One of the most misunderstood groups is dietary fats and oils, leading to confusion among people.
Common Misconceptions
A widespread but incorrect belief is that “animal tallow (sheep fat) is natural and does not increase blood fat, while vegetable and industrial oils are carcinogenic.” This belief is fundamentally flawed. Animal tallow, as a type of animal fat, predominantly contains saturated fats.
Excessive consumption of saturated fats is associated with:
- Elevated levels of bad cholesterol (LDL) in the blood,
- Increased risk of cardiovascular diseases,
- Higher likelihood of certain cancers and mortality related to these conditions.
Global Dietary Guidelines
According to global dietary guidelines:
- Saturated fat consumption should be limited to less than 10% of total daily energy intake.
- Vegetable oils, being predominantly unsaturated fats, are considered healthier. These oils contain very low trans fat levels, often less than 0.5%.
Benefits of Vegetable Oils
When stored and used properly, and consumed in moderation, vegetable oils can contribute to better health. For example:
- Olive oil is often recommended for its role in cancer prevention.
- Unsaturated fatty acids in these oils are beneficial but susceptible to oxidation, which can create harmful compounds if mishandled.
Oxidation and Safety Measures
Unsaturated fats in vegetable oils are prone to oxidation when exposed to excessive heat or prolonged use, potentially forming carcinogenic compounds. To counteract this:
- In industrial production, antioxidants such as vitamin E are added to prevent oxidation.
- For home use, it is essential to avoid excessive heating or prolonged cooking with liquid oils to preserve their health benefits and minimize risks.
Conclusion
By understanding the properties and proper usage of fats and oils, we can debunk common myths and make informed dietary choices that promote health and prevent disease. Always prioritize moderation, proper storage, and cooking practices to maximize the benefits of vegetable oils while minimizing potential risks.