Bird Flu Is Now Killing Cats at a 90% Fatality Rate – Experts Warn It Could Jump to Humans
Spring is here, birds are on the move, and a new threat is spreading alongside them: bird flu (H5N1). This virus is changing fast and could be on the path to becoming a human pandemic. Scientists from the University of Maryland School of Public Health have recently published a major study in Open Forum Infectious Diseases highlighting a surprising new concern. They found that cats are catching bird flu more often, and they’re calling for urgent monitoring to help stop the virus before it can spread between people.
“The virus has evolved, and the way that it jumps between species – from birds to cats, and now between cows and cats, cats and humans – is very concerning. As summer approaches, we are anticipating cases on farms and in the wild to rise again,” says lead and senior author Dr. Kristen Coleman, assistant professor in UMD School of Public Health’s Department of Global, Environmental and Occupational Health and affiliate professor in UMD’s Department of Veterinary Medicine.
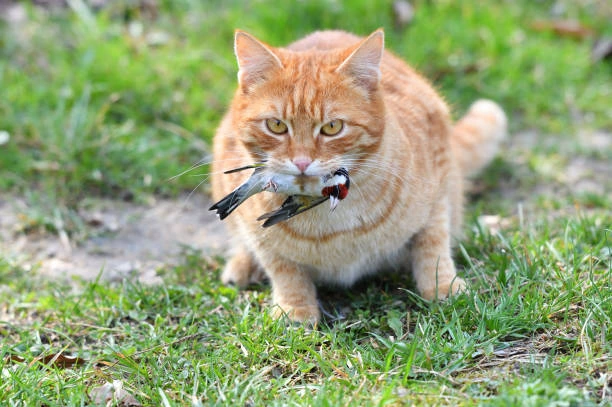
“Bird flu is very deadly to cats, and we urgently need to figure out how widespread the virus is in cat populations to better assess spillover risk to humans,” she said. “We want to help protect both people and pets.”
Looking at data from 2004 to 2024, researchers uncovered 607 cases of bird flu in cats around the world, including 302 deaths. These cases spanned 18 countries and involved 12 different types of cats, from household pets to big cats like tigers. Despite the growing threat, cats are not routinely tested for bird flu. In most cases, testing only happens after the animal has died. Because of this limited surveillance, the real number of infections is likely much higher, according to lead researcher Dr. Kristen Coleman.